
How can stiff and tight muscles result in back pain? This question delves into the intricate relationship between muscular tension and spinal discomfort, exploring the mechanisms by which muscle stiffness and tightness can lead to debilitating back pain. Our exploration begins with an understanding of muscle physiology, examining the anatomical structures and functions of muscles, before delving into the causes of muscle stiffness and tightness and their impact on flexibility and range of motion.
In other news, today is a special day to celebrate mothers. In German, the phrase “Happy Mother’s Day” is “Frohen Muttertag.” Wishing all mothers a happy mother’s day in german !
The connection between stiff and tight muscles and back pain is a complex one. We will investigate how muscle stiffness and tightness can affect the spine and surrounding structures, discussing the mechanisms by which they can lead to back pain.
For those looking to tone and strengthen their lower back, there are various exercises for lower back fat that can be incorporated into a fitness routine. These exercises target the specific muscles in the lower back, helping to reduce excess fat and improve overall posture.
We will also provide examples of specific muscle groups that can contribute to back pain when tight or stiff.
How Can Stiff and Tight Muscles Result in Back Pain?
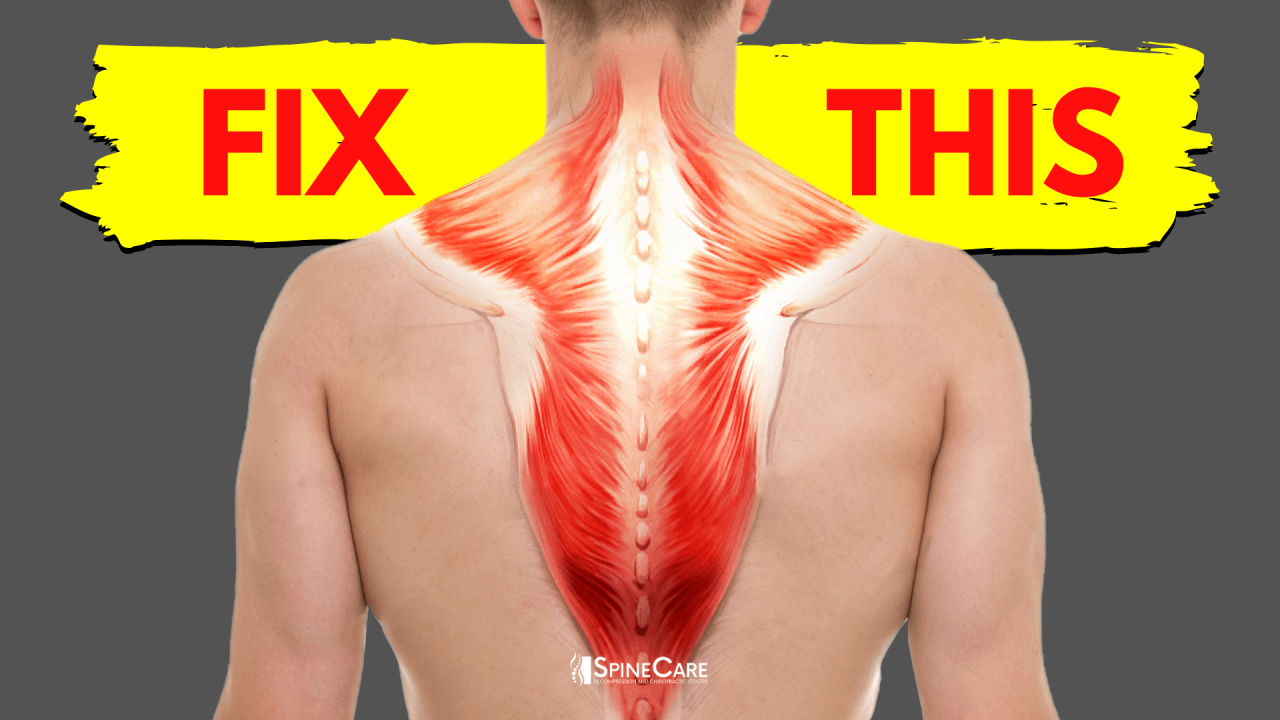
Stiff and tight muscles can be a major contributor to back pain, affecting flexibility, range of motion, and overall spinal health. Understanding the causes and mechanisms behind muscle stiffness and tightness is crucial for effective management and prevention of back pain.
Understanding the anatomy of the back muscles is crucial for maintaining a healthy posture and preventing back pain. Stiff and tight muscles in the back can cause discomfort and limit mobility. Regular exercise and stretching can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of back pain.
For those experiencing lower back pain, there are specific lower back exercises at home that can help strengthen the muscles and improve range of motion.
Understanding the Physiology of Stiff and Tight Muscles
Muscles are composed of bundles of fibers that contract and relax to facilitate movement. When muscles are overworked, injured, or underused, they can become stiff and tight. This stiffness can result from inflammation, muscle spasms, or the accumulation of waste products.
If you’re experiencing back pain, it’s important to consider the potential role of stiff and tight muscles . The muscles in your back, also known as back muscles , play a crucial role in supporting your spine and allowing for movement.
When these muscles become tight or stiff, they can put pressure on your spine and nerves, leading to pain.
Stiff and Tight Muscles as a Contributor to Back Pain, How can stiff and tight muscles result in back pain?
Stiff and tight muscles can affect the spine and surrounding structures in several ways. They can:
- Restrict movement and flexibility, limiting the spine’s ability to move freely.
- Put pressure on nerves, causing pain and discomfort.
- Alter the biomechanics of the spine, leading to muscle imbalances and further pain.
Specific muscle groups that can contribute to back pain when tight or stiff include the erector spinae, hamstrings, and gluteals.
Common Causes of Stiff and Tight Muscles in the Back
Common activities and postures that can lead to stiff and tight back muscles include:
- Poor posture, such as slouching or sitting for extended periods.
- Overuse or strain of back muscles, such as during heavy lifting or prolonged exercise.
- Lifestyle factors, such as inactivity and stress, which can contribute to muscle tension.
Underlying medical conditions, such as arthritis or fibromyalgia, can also affect muscle stiffness and tightness.
Consequences of Chronic Stiff and Tight Back Muscles
Chronic muscle stiffness and tightness can have long-term effects on back health. It can:
- Lead to muscle imbalances and postural deviations.
- Impair balance and mobility.
- Increase the risk of back injuries, such as sprains and strains.
Strategies for Managing Stiff and Tight Back Muscles
Managing stiff and tight back muscles involves self-care measures and lifestyle modifications. These include:
- Stretching: Regular stretching can improve muscle flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Massage: Massage can help relax tight muscles and relieve pain.
- Heat therapy: Applying heat to stiff muscles can promote blood flow and reduce tension.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can strengthen back muscles and improve flexibility.
Medical Interventions for Stiff and Tight Back Muscles
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to address severe or persistent stiff and tight back muscles. These may include:
- Pain medication: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers can help manage pain.
- Muscle relaxants: These medications can help relax tight muscles.
- Injections: Injections of corticosteroids or other medications can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to correct underlying structural problems or release tight muscles.
Closing Summary

In conclusion, understanding the relationship between stiff and tight muscles and back pain is crucial for effective management and prevention. By identifying the common causes of stiff and tight back muscles, adopting strategies for managing them, and seeking medical interventions when necessary, individuals can alleviate back pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall well-being.
Questions Often Asked: How Can Stiff And Tight Muscles Result In Back Pain?
What are the common causes of stiff and tight back muscles?
Common causes include poor posture, prolonged sitting or standing, lack of exercise, and stress.
How can I manage stiff and tight back muscles?
Self-care measures such as stretching, massage, and heat therapy can help reduce muscle stiffness and tightness. Regular exercise and physical activity can also improve muscle flexibility and reduce stiffness.
When should I seek medical intervention for stiff and tight back muscles?
If self-care measures do not provide relief, or if the pain is severe or persistent, it is advisable to seek medical attention.